What Is Palliative Care And How Does It Differ from Hospice Care?
Palliative and Hospice care both provide improved quality of life, support for families, and coordinated care.It’s crucial to understand the differences between palliative care and hospice care,

When facing a serious illness, navigating the healthcare landscape can be overwhelming. It’s crucial to understand the differences between palliative care and hospice care, two approaches that aim to improve the quality of life for patients and their families. With a fresh perspective on these types of care, we’ll explore their unique benefits, how they compare, and how to choose the right approach for your loved one.
Short Summary
- Palliative and Hospice care both provide improved quality of life, support for families, and coordinated care.
- Knowing the eligibility requirements & timing can help make the right decision for loved one’s care.
- Talking to healthcare providers & understanding differences between Palliative & Hospice Care helps choose best option.
Understanding Palliative Care

Palliative care is specialized medical care for individuals with serious illnesses, focusing on enhancing their quality of life and providing relief from symptoms and stress. This type of care is all about addressing the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients, helping them make informed decisions about their medical treatment.
But how does palliative care compare to hospice care, another option for those facing serious illness?
Who Can Benefit from Palliative Care?
Palliative care is suitable for anyone with a serious illness, regardless of the stage, and can be provided alongside curative treatments. This means that patients receiving palliative care can still pursue aggressive treatments to combat their illness while benefiting from symptom management and enhanced quality of life.
This approach sets it apart from hospice care, which is designed for patients with a life expectancy of six months or less.
The Palliative Care Team

The palliative care team is a group of healthcare professionals who come together to provide specialized care to individuals with serious illnesses. This team typically includes doctors, nurses, social workers, chaplains, and other trained specialists from a palliative care organization. They provide expert care for managing pain and other symptoms, discuss treatment options, and offer emotional support for the patient and their family.
Hospice care, on the other hand, also offers similar support, but specifically, hospice care focuses on patients in the end-of-life stage through a well-designed hospice program.
Where is Palliative Care Provided?
Palliative care can be offered in various settings, such as hospitals, outpatient clinics, and even at home. The care is provided by a team of healthcare professionals, who work with the patient, their family, and other providers to offer relief from physical, emotional, social, and spiritual pain.
Coverage for palliative care may be provided by Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance, depending on the patient’s specific plan and needs.
Hospice Care: An Overview

Hospice care is a compassionate approach to end-of-life care, focusing on comfort and quality of life when curative treatments are no longer effective. Similar to palliative care, hospice care aims to provide relief from pain, fatigue, nausea, and the stress that comes with a serious illness or the side effects of medical treatment. By utilizing hospice services and the hospice benefit, patients can receive the support they need during this difficult time.
However, the hospice care approach is specifically tailored for hospice patients nearing the end of life.
When is Hospice Care Appropriate?

Hospice care is suitable for patients with a life expectancy of six months or less, as determined by their doctor and a hospice medical director. This type of care is designed to prioritize comfort and quality of life for patients in their final months, providing emotional and practical support for both the patient and their family members.
While some may resist hospice care due to feelings of “giving up” or losing hope, it’s important to recognize that this compassionate approach offers patients an opportunity for dignity and comfort in their final days.
The Hospice Care Team

The hospice team, which provides hospice care, is made up of core members like doctors, nurses, and social workers, as well as any other specialists that might be needed. This team provides medical, emotional, and spiritual support for the patient and their family, ensuring that their needs are met throughout the end-of-life process.
Hospice care teams, which include hospice providers, also offer respite care, giving family caregivers a much-needed break to rest and recharge.
Where is Hospice Care Provided?

Hospice care can be provided in various places, such as at home, in hospitals, extended-care facilities, or inpatient hospice centers, depending on what the patient needs and wants. Tailoring the care setting to the patient’s preferences ensures that they receive the most comfortable and supportive care possible during their final days.
Similar to palliative care, hospice care coverage depends on the patient’s insurance plan, with Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance often providing coverage for eligible patients.
Comparing Palliative Care and Hospice Care

While both palliative and hospice care aim to improve the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses, there are differences in their goals, eligibility, and coverage. Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms and providing relief at any stage of illness, while hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life at the end of life when curative treatments are no longer effective.
Understanding these distinctions can help families make informed decisions about the best approach for their loved one’s care.
Goals of Care

Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms and providing relief, aiming to enhance the quality of life for those with serious illnesses. This type of care addresses the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients, as well as provides relief from pain and other symptoms.
In contrast, hospice care prioritizes comfort and quality of life at the end of life, ensuring that patients receive the necessary support and care during their final days.
Eligibility and Timing

Palliative care is available at any stage of illness, making it an option for patients dealing with a wide range of serious illnesses, such as heart failure, COPD, cancer, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and more. Hospice care, on the other hand, is specifically for patients with a life expectancy of six months or less, as determined by their doctor and a hospice medical director.
Being aware of these eligibility criteria can help families make the right choice for their loved one’s care.
Coverage and Costs
Both palliative and hospice care may be covered by Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance, with varying levels of out-of-pocket expenses. While coverage for palliative care depends on the patient’s insurance plan, hospice care is often covered by Medicare or other insurance companies for eligible patients.
Understanding the potential costs and coverage options for each type of care can help families make informed decisions about the best approach for their loved one’s needs.
The Benefits of Palliative and Hospice Care

Both palliative and hospice care provide improved quality of life, support for families, and coordinated care for individuals suffering from serious illnesses. By addressing the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients and their families, these types of care offer a holistic approach to managing the challenges of serious illness.
Let’s take a closer look at some of the specific benefits that each type of care offers.
Improved Quality of Life
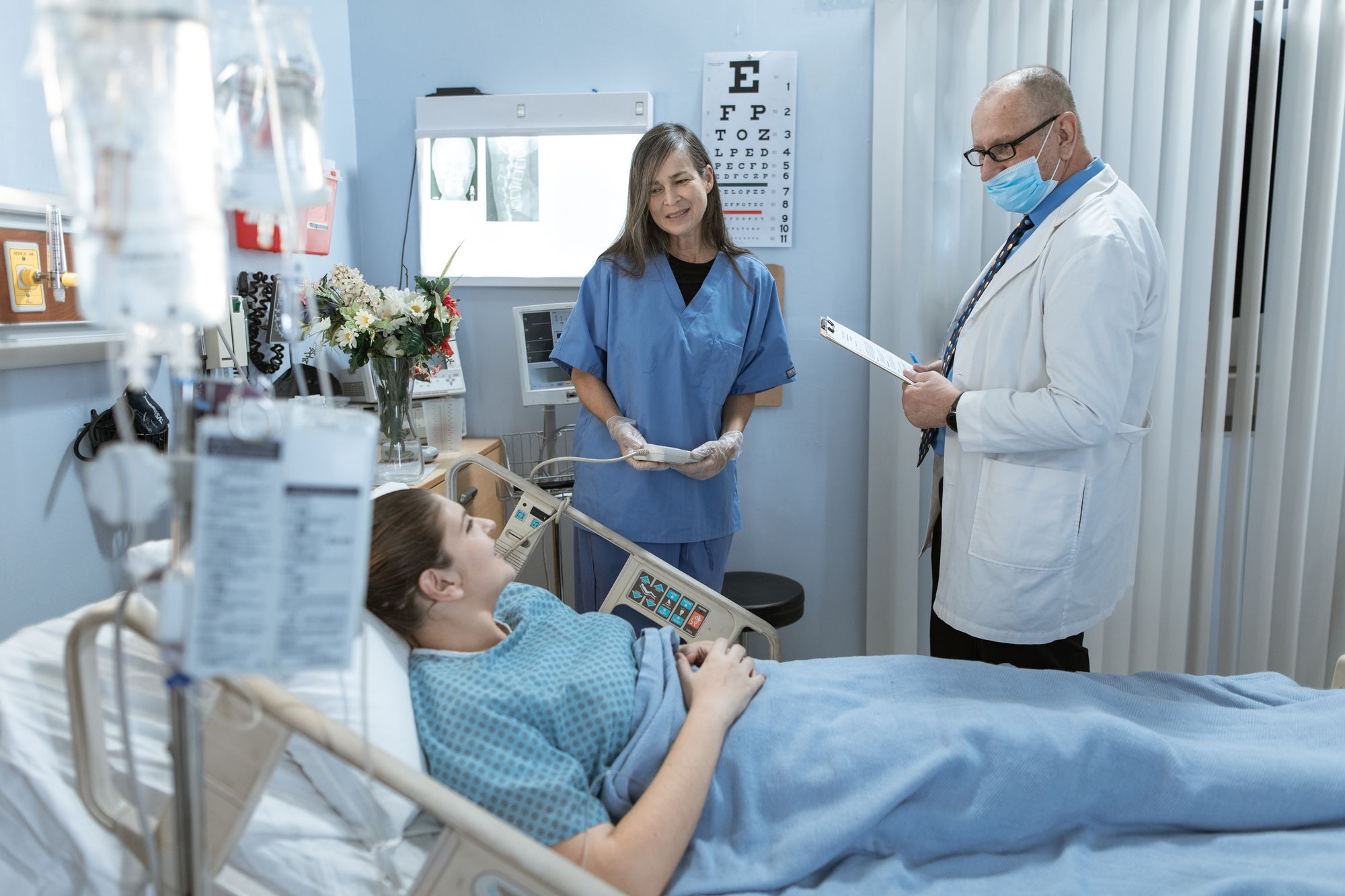

Palliative and hospice care both focus on managing pain, symptoms, and stress, leading to better overall well-being for patients. By providing medications, therapies, and other medical supplies, these types of care can help reduce discomfort and improve quality of life for patients and their families.
This emphasis on symptom management and relief, as opposed to curative treatment, allows patients to maintain a higher level of comfort and functionality throughout their illness.
Support for Families

Both types of care provide emotional, practical, and spiritual support for patients’ families, including bereavement care after the patient’s death. This support helps families cope with the emotional challenges of caring for a loved one with a serious illness and provides them with the resources and guidance they need to make informed decisions about their loved one’s care.
Additionally, palliative and hospice care teams offer respite care, giving family caregivers a much-needed break to rest and recharge.
Coordination of Care
Palliative and hospice care teams work together with other healthcare providers to ensure seamless, comprehensive care for patients. This coordination of care includes making sure medications, treatments, and other services are appropriately managed to ensure the patient’s needs are met.
By working closely with other healthcare providers, palliative and hospice care teams can help patients receive the best possible care during their illness.
How to Choose Between Palliative and Hospice Care

Discussing options with healthcare professionals, considering the patient’s goals and preferences, and understanding the differences between palliative and hospice care can help families make informed decisions about the best approach for their loved one. By taking the time to explore the unique benefits and eligibility criteria for each type of care, families can ensure that their loved one receives the most appropriate and supportive care during their illness.
Palliative care focuses on symptom management and comfort, while hospice care is designed to improve the quality of life.
Summary
In conclusion, both palliative and hospice care offer comprehensive, compassionate approaches to managing serious illnesses and improving quality of life for patients and their families. By understanding the differences between these two types of care and working closely with healthcare professionals, families can make informed decisions about the best approach for their loved one’s care. Ultimately, the choice between palliative and hospice care will depend on the patient’s unique needs, goals, and preferences, but both options provide valuable support during challenging times.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is difference between hospice and palliative care?
Palliative care is available to all patients at any time during their illness and may include curative intent, while hospice care is reserved for terminally ill patients who have 6 months or less to live and does not include curative intent.
Hospice care focuses on providing comfort and support to the patient and their family, rather than trying to cure the illness. It is designed to help the patient and their family cope with the physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects of the end of life.
Is palliative care considered end of life care?
No, palliative care is not the same as end of life care. It is a broader term that can last for longer and doesn’t necessarily mean someone is close to dying.
What are the 3 forms of palliative care?
Palliative care comes in three main forms: physical, psychological and spiritual. Each of them has its own unique role to play in a treatment plan.
What are examples of palliative care?
Palliative care is a form of treatment for many chronic illnesses, such as cancer, heart failure, dementia and more. It focuses on symptom relief and helping families cope with difficult decisions as the illness progresses, including providing support to caregivers.
Additionally, palliative care can include treatments for anxiety and other symptoms related to the disease.
What's the meaning of hospices?
Hospice is a special type of care that focuses on providing comfort, support and dignity to people facing a terminal illness. It typically provides palliative care in a home-like setting, with the aim of maximizing quality of life for the patient and their family.
The goal of hospice is to provide physical, emotional, and spiritual support to the patient and their family. It is a holistic approach to care that focuses on the patient’s quality of life, rather than on the patient’s quality of life.
You might also like this article:






