Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Medication: Understanding Types, Treatments, and Cost Savings
Explore our Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes Medication, covering types, treatments, and how MyFreePharmacyPlan.org reduces costs. Learn about managing diabetes effectively with affordable medication, testing supplies, and free resources.

Diabetes is a chronic condition impacting millions worldwide, with two primary types: Type 1 and Type 2. Effective management often involves medication, and understanding these options is crucial for those living with diabetes. Additionally, programs like MyFreePharmacyPlan.org's Save On Diabetes offer significant cost savings, making diabetes care more accessible and affordable.
Understanding Types of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy, playing a vital role in regulating blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults but can occur at any age.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
Autoimmune Reaction
Type 1 diabetes is often caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune destruction can be influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors
While the exact cause of Type 1 diabetes is still unknown, genetics plays a significant role. Individuals with a family history of Type 1 diabetes have a higher risk of developing the condition.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors, such as viral infections, might also play a role. Some theories suggest that a virus can trigger the immune system to attack the pancreas.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
Symptoms
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can develop quickly, over a few weeks or months, particularly in children. They include increased thirst and urination, hunger, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and in some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis—a potentially life-threatening condition due to the buildup of acids (ketones) in the blood.
Diagnosis
Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed through various blood tests that measure blood sugar levels. These tests can include the glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test, random blood sugar test, fasting blood sugar test, and an autoantibody test to confirm an autoimmune process.
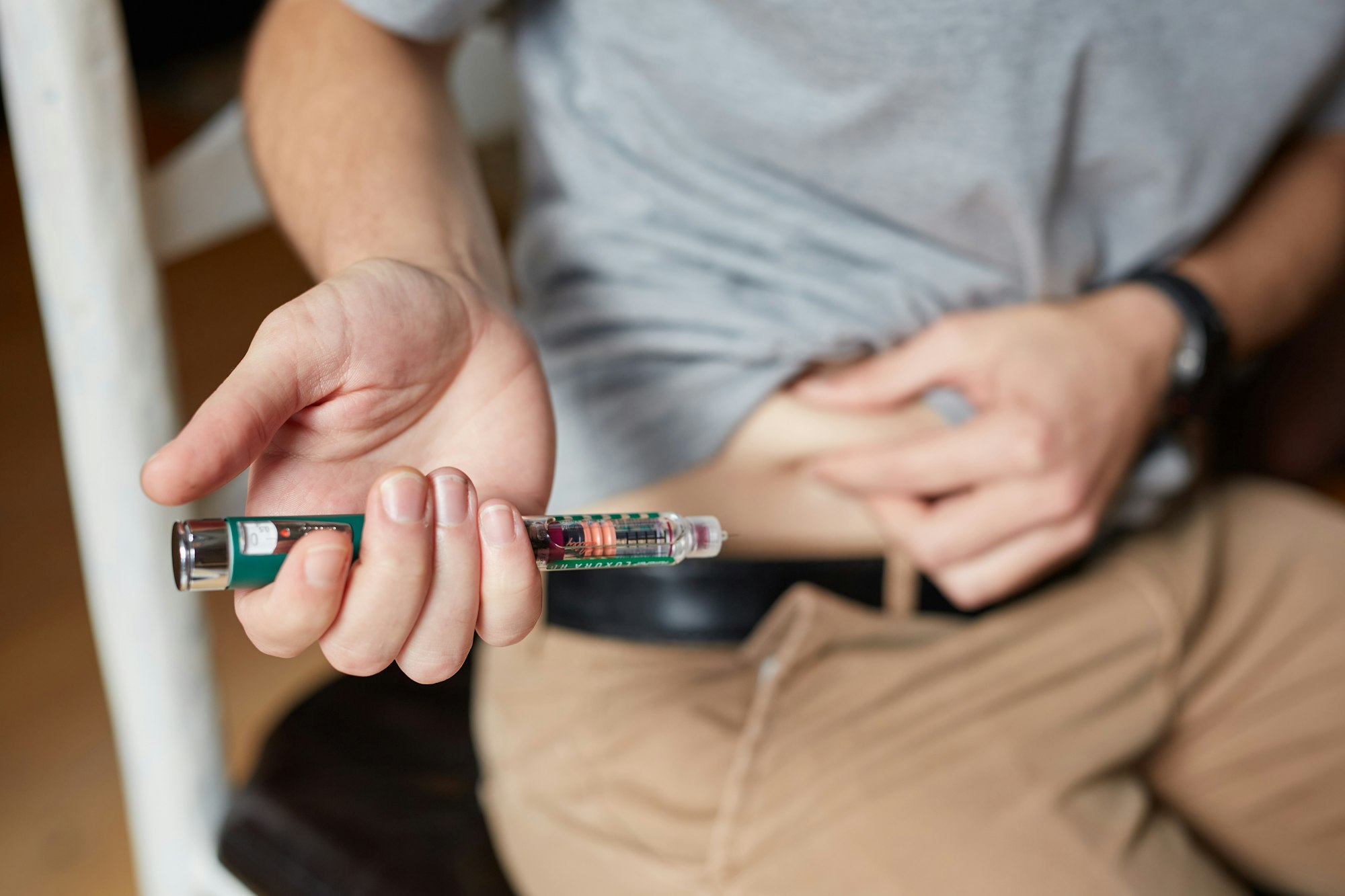

Treatment and Management
Insulin Therapy
Since the body cannot produce insulin, treatment for Type 1 diabetes centers around insulin therapy. Insulin can be administered through injections with a syringe, insulin pen, or an insulin pump, which delivers constant insulin through a small tube placed under the skin. Learn about the Save on Diabetes program to find out how you can get the lowest prices of insulin in the US.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for people with Type 1 diabetes. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems are increasingly used for real-time blood sugar tracking.
Diet and Exercise
Diet and physical activity are important parts of managing Type 1 diabetes. Balancing insulin doses with food intake and physical activity levels is crucial. Carbohydrate counting and meal planning can help manage blood sugar levels.
Education and Support
Education about the condition, treatment options, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial for individuals with Type 1 diabetes. Support from healthcare providers, family, and diabetes support groups can also play a significant role in effective management.
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires careful and continuous management. Advances in insulin therapy and blood glucose monitoring have significantly improved the quality of life for individuals with Type 1 diabetes. While it is a challenging condition, with the right tools and support, individuals with Type 1 diabetes can lead full and active lives.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Resistance
In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar. Insulin resistance means that although the body is producing insulin, the cells do not respond to it effectively. This leads to higher blood sugar levels as glucose accumulates in the bloodstream instead of being used for energy.
Gradual Onset
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which typically appears suddenly and at a younger age, Type 2 diabetes develops gradually and is more commonly diagnosed in adults, although it is increasingly seen in children, adolescents, and young adults due to rising obesity rates.
Causes and Risk Factors
Lifestyle Factors
Type 2 diabetes is strongly associated with lifestyle factors. The following are significant contributors:
- Obesity and Overweight: Excess body fat, especially around the waist, increases the risk of developing insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise contributes to weight gain and can increase insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in calories, processed foods, and sugar can contribute to the development of Type 2 diabetes.
Genetic Factors
Genetics also plays a role. People with a family history of Type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of developing the condition. Certain ethnic groups are also at a higher risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
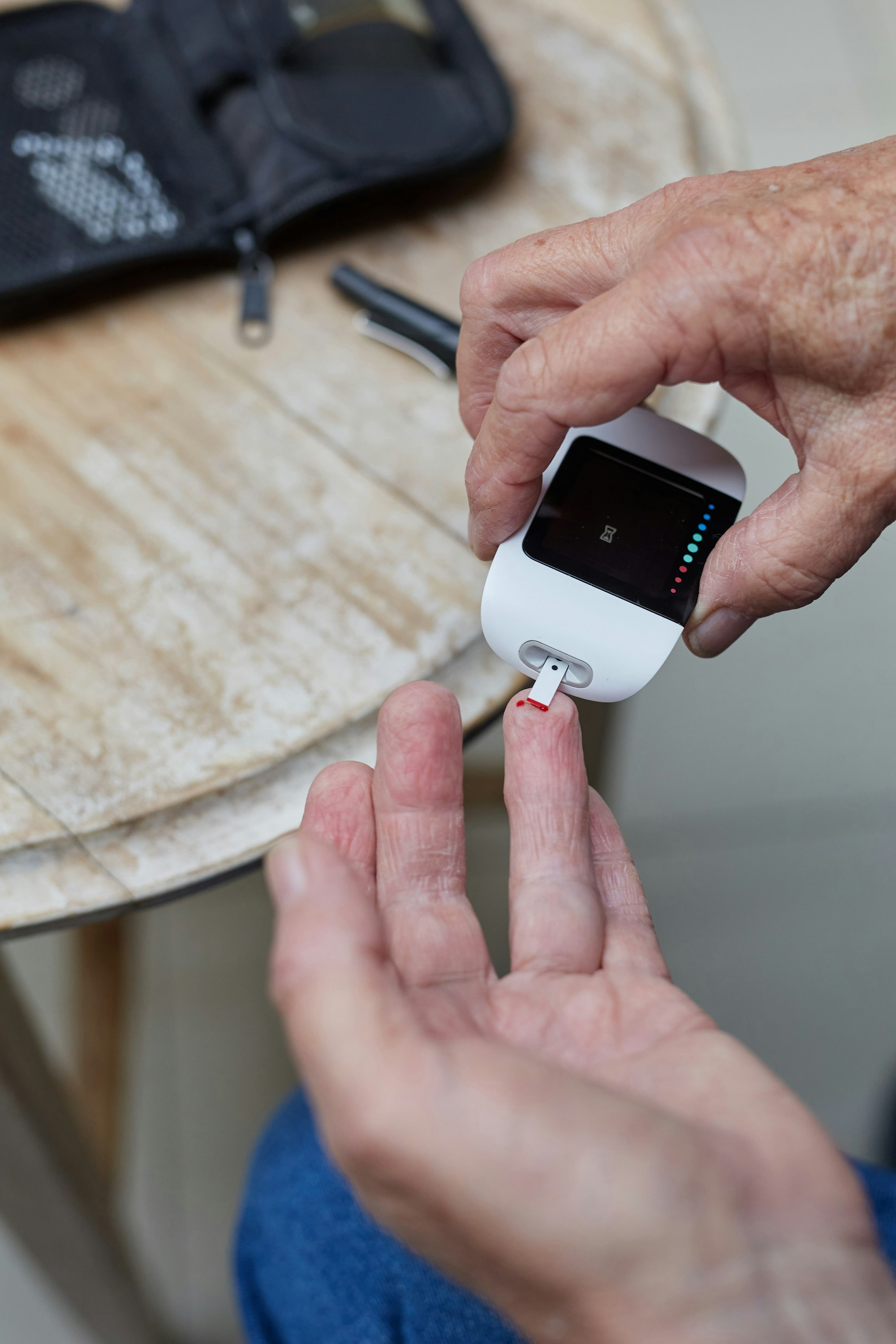

Symptoms
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes develop slowly and can include increased thirst, frequent urination, hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of wounds. Some people may not experience symptoms in the early stages.
Diagnosis
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels. These include the A1C test, fasting blood sugar test, and glucose tolerance test.
Management and Treatment
Lifestyle Changes
Diet and exercise are foundational in managing Type 2 diabetes. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, combined with regular physical activity, can significantly control blood sugar levels.

Medication to Treat Type 2 Diabetes
When diet and exercise are not sufficient to manage blood sugar levels, medications are prescribed. These can include:
- Metformin: Helps reduce glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: Increases insulin production from the pancreas.
- DPP-4 Inhibitors: Helps to reduce blood sugar levels without causing weight gain.
- Insulin Therapy: Some individuals with Type 2 diabetes may require insulin.
Type 2 diabetes is a complex condition with multiple contributing factors. Its management requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and medication as needed. Early diagnosis and proactive management are key to preventing complications and maintaining good health.
I want to address the growing Pre Diabetes Epidemic
Pre-diabetes is a health condition characterized by blood sugar levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It is a warning sign indicating a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Pre-diabetes is often a precursor to type 2 diabetes unless interventions are made to control blood sugar levels.
Understanding Pre-diabetes
Blood Sugar Levels in Pre-diabetes
- Fasting Blood Sugar Levels: Typically, fasting blood sugar levels in pre-diabetes range from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L).
- A1C Levels: The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months. An A1C level of 5.7% to 6.4% is considered pre-diabetes.
Diagnosis of Pre-diabetes
Pre-diabetes is usually diagnosed through one or more of the following blood tests:
1. Fasting Plasma Glucose Test
This test measures blood sugar after an overnight fast. Blood sugar levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL indicate pre-diabetes.
2. A1C Test
This test provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three months. An A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% is indicative of pre-diabetes.
3. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test
This test involves fasting overnight, having a blood sugar level measured, drinking a sugary liquid, and then having blood sugar levels checked again after two hours. A reading between 140 and 199 mg/dL after two hours suggests pre-diabetes.
Treatment and Management of Pre-diabetes

Lifestyle Changes
The primary treatment for pre-diabetes involves making lifestyle changes:
Diet
Healthy Eating: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit intake of processed foods, high-sugar items, and excessive carbohydrates.
Portion Control: Managing portion sizes can help regulate calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight.
Exercise
Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in moderate physical activity such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes a week can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Weight Loss
Weight Management: Losing 5% to 7% of body weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is advised to keep track of any changes that might indicate progression towards type 2 diabetes.
Medication
In some cases, particularly when lifestyle changes are not enough or if there is a high risk of developing diabetes, doctors might recommend medication such as metformin, which can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
Pre-diabetes is a serious health condition, but it can be managed and even reversed with the right lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and intervention are key to preventing the progression to type 2 diabetes and reducing the risk of other associated health complications. Regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare providers are essential steps in managing pre-diabetes.
Navigating the Costs of Diabetes Management with the Save On Diabetes Program

Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires continuous management, including regular blood sugar monitoring, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. However, the cost of treating diabetes – including testing supplies, lancets, pills, and insulin – can be a significant financial burden for many. Recognizing this challenge, MyFreePharmacyPlan.org has introduced the Save On Diabetes program, a comprehensive initiative designed to ease the financial strain for diabetes patients.
The Cost of Managing Diabetes
Testing and Monitoring Expenses
- Blood Glucose Meters and Test Strips: Regular blood glucose monitoring is vital for diabetes management, but the cost of meters and test strips can add up quickly.
- Lancets and Lancing Devices: Used for blood sampling, these are recurring expenses as they need to be replaced regularly for effective and safe blood glucose monitoring.
Medication Costs
- Oral Medications: Pills for managing diabetes, such as metformin or sulfonylureas, are ongoing expenses.
- Insulin Therapy: For many, especially those with Type 1 diabetes, insulin is a life-saving medication. However, the cost of insulin can be prohibitively expensive, particularly for those without insurance or with limited coverage.
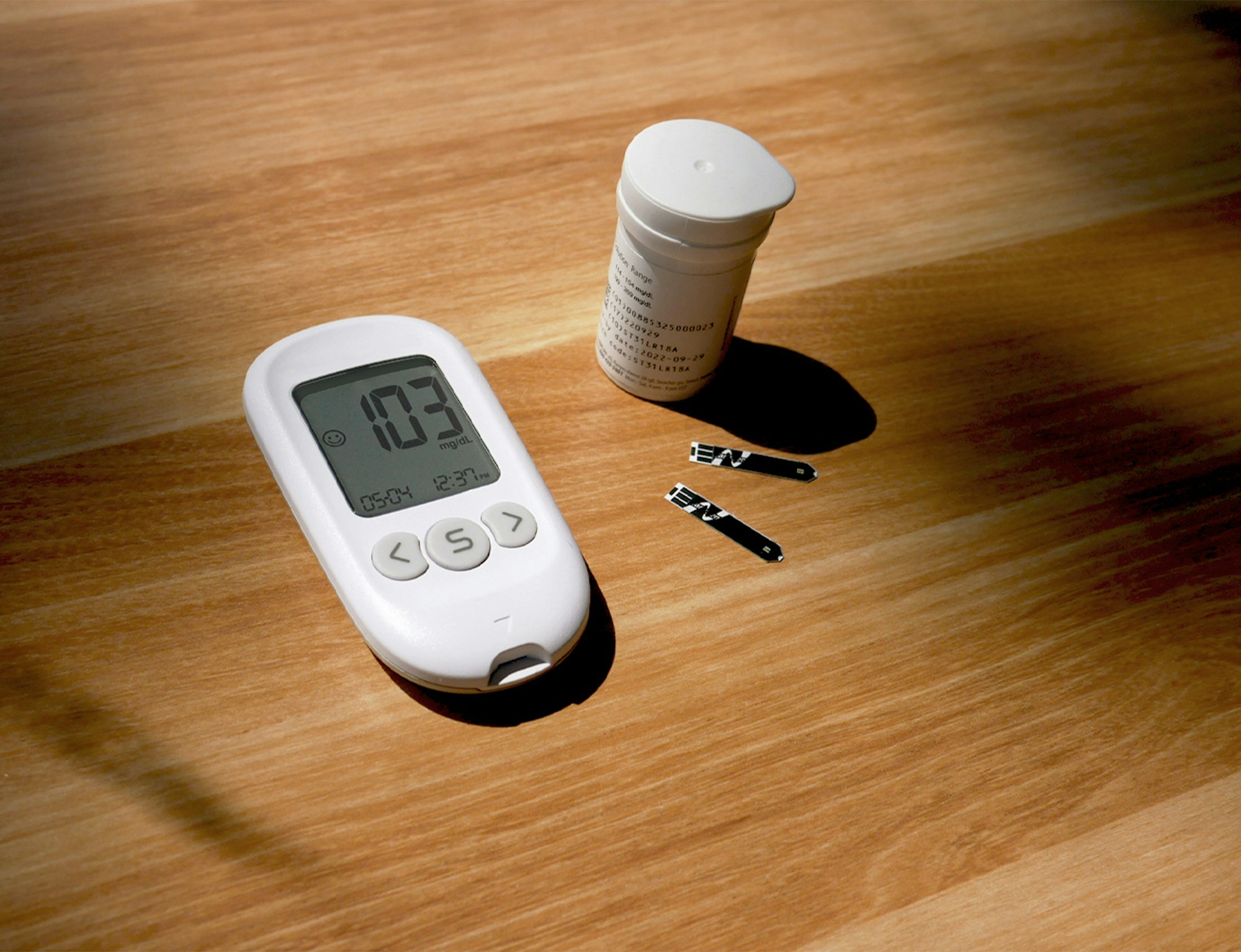
The Save On Diabetes Program by MyFreePharmacyPlan.org
A Comprehensive Support for Program Diabetes Patients
The Save On Diabetes program is a revolutionary approach to reduce the costs associated with diabetes management.
Free Starter Kit and Diabetes Prescriptions
- Free Premium Bilingual Voice-Response Glucometer: A state-of-the-art glucometer provided at no cost.
- 3-Month Supply of Test Strips: Essential for regular blood glucose monitoring.
- Supply of Lancets, Lancing Device, and Control Solution: These necessary supplies are included, reducing the need for additional purchases.
- $0 Out-of-Pocket on Listed Diabetes Medications: This feature significantly lowers the financial burden of ongoing diabetes management. Please visit Save on Diabetes Program to learn more about the diabetes medications and supplies available to you.
Lowest Priced Insulin in the United States
Through a partnership with Walmart, the program offers insulin vials (ReliOn™ Novolin 70/30, N, and R) at the lowest prices in the country, making insulin more accessible to those who need it.
Accessibility and Convenience
- Over 5200 Walmart Locations for Pickup: Easy access to prescribed insulin.
- Free Shipping: Direct delivery of supplies to your mailbox, adding convenience and further cost savings.
Importance of the Save On Diabetes Program
With diabetes affecting a large portion of the population and one in three Americans being pre-diabetic, programs like Save On Diabetes are not just financially beneficial; they are essential for public health. By providing affordable access to vital monitoring equipment and medications, MyFreePharmacyPlan.org’s initiative plays a crucial role in helping individuals manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
The cost of diabetes management can be daunting, but the Save On Diabetes program provides a practical and affordable solution. By offering free meters, low-cost testing supplies, and affordable medication options, this program is a game-changer in diabetes care. It represents a significant step towards easing the financial challenges faced by individuals living with diabetes and ensuring that everyone has access to the necessary tools for effective disease management.
If you want to become a representative please click here
Looking for cost effective products for diabetes? Click here
Please note that some of the links on our site are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, we may receive a commission at no extra cost to you. We recommend these products because of their quality and not because of the commission we receive from your purchases. The decision is yours, and whether or not you decide to buy something is completely up to you.




