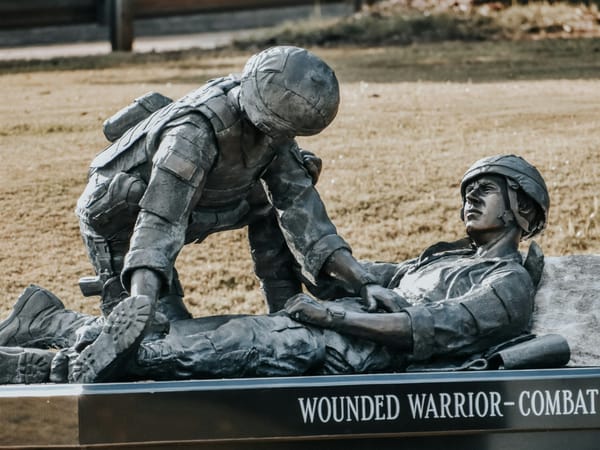
Silent Aspiration in the Elderly: Preventing Swallowing Problems
Silent aspiration occurs when food or liquid enters the lungs without obvious symptoms like coughing, increasing the risk of pneumonia in the elderly. Understanding the signs, risks, and prevention strategies is crucial for caregivers to ensure safe swallowing.

Did you know that the silent aspiration elderly is a serious but often overlooked issue that can lead to severe complications in older adults? With age, the ability to swallow may decline due to weakened muscles and reduced reflexes. Many elderly patients with neurological disorders experience silent aspiration, which significantly increases the risks of swallowing difficulties and pneumonia. Statistics indicate that a significant percentage of this population experiences silent aspiration, worsening their overall health outcomes. In this blog post, we’ll explore what the silent aspiration elderly is, its causes, and its effects on elderly patients. I want to explain that dysphagia is the medical term for swallowing problems.
Let’s delve into ways to identify these swallowing problems, strategies to prevent silent aspiration, medical interventions, and the vital role of healthcare professionals in dealing with this issue. So let’s dive in and learn how to protect our elderly loved ones from the dangers of silent aspiration in the elderly!
Silent Aspiration in Elderly Preventing Swallowing Problems
Definition and Prevalence
Silent aspiration is a condition where food, liquids, or other substances enter the airway without any noticeable symptoms, such as coughing or choking. This condition is particularly common among older adults, especially those with swallowing disorders or dysphagia. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA), dysphagia affects approximately 15 million Americans, with a significant portion being older adults. Silent aspiration can lead to serious complications, including aspiration pneumonia, a type of pneumonia caused by the inhalation of foreign materials into the lungs. Understanding the prevalence and risks associated with silent aspiration is crucial for early detection and prevention.
Short Summary
- Silent aspirations in elderly patients can be prevented by recognizing signs of dysphagia or swallowing problems and understanding risk factors that contribute to the risk of aspiration.
- Strategies such as modifying oral intake, meaning offering varying types of thickened liquids. providing feeding assistance, this may include learning the chin tuck method and swallowing therapy help reduce the risk of silent aspiration.
- Healthcare professionals, such as a speech therapist play an important role in preventing silent aspiration through therapies and monitoring for risks.
Understanding Silent Aspiration Signs
Silent aspiration occurs when food or liquid enters the lungs without any obvious signs, leading to potential complications like aspiration pneumonia. It is more common in elderly patients due to age-related changes in swallowing reflexes and tongue control.
Aspiration is a symptom of dysphagia, a condition where someone has trouble swallowing. Recognizing the aspiration signs and symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, and a hoarse voice. Knowing aspiration signs is crucial as it can help detect swallowing disorders and prevent complications like pneumonia and pulmonary edema.
Causes of Silent Aspiration
There are various factors that can increase the risk of aspiration. The oral cavity can harbor pathogenic organisms, which, if aspirated, may lead to aspiration pneumonia. For example, certain medical conditions like Parkinson’s disease, post-stroke, and dementia increase the risk of dysphagia and aspiration. Age-related changes in swallowing may also play a role, as one study looked into aging-related swallowing issues hospitalized adults as part of systematic review of their nursing interventions.
Moreover, eleven studies focused on residents with different levels of swallowing difficulties, aiming to improve their swallowing ability and prevent aspiration pneumonia. Stimulation treatment, which uses thermal or mechanical stimulation at the front of the throat to trigger a reflex swallowing action, has also been found to help prevent aspiration pneumonia.
Effects on Elderly Patients
Silent aspiration can have a significant impact on elderly patients. Older adults with feeding tubes, for example, are at a higher risk for aspiration, leading to other symptoms such as respiratory complications. Moreover, the intervention in one study was specifically aimed at frail residents, emphasizing the need for targeted approaches to prevent aspiration in vulnerable elderly persons. I hope you will read my article on the Pros and Cons of Feeding Tubes in the Elderly.
By understanding the effects of silent aspiration on elderly stroke patients, or those with other neurological conditions, or even dental problems healthcare professionals can better tailor their interventions. This will help them create care plans to reduce the risk of complications and improve the quality of life for these individuals.
Identifying Swallowing Problems in Older Adults
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is a common symptom of silent aspiration in older adults. Recognizing the signs of dysphagia, such as coughing, choking, having excessive oropharyngeal secretions that cause drooling, and changes in speech, is crucial in identifying and managing this condition.
Furthermore, several risk factors can contribute to dysphagia, including stroke, Parkinson's disease acute stroke, dementia, and other medical conditions. Early identification of dysphagia and its risk factors is essential in preventing silent aspiration and its complications in elderly patients and improve patient care.
Common Symptoms

Older adults with dysphagia may experience various symptoms that can help identify the presence disease severity of a swallowing disorder. These symptoms include difficulty swallowing, coughing, choking, drooling, and changes in speech.
Additionally, they may also experience regurgitation, malnutrition, dehydration, trouble breathing and weight loss. Being aware of these common symptoms can help health care professionals and caregivers identify dysphagia in older adults and take appropriate steps to prevent silent aspiration and its complications.
Risk For Aspiration
There are numerous risk factors that contribute to dysphagia in older adults. Aging, age-related diseases, dental problems, dull neuroreceptors, a decrease in salivary secretion and the elasticity of swallowing organs, frailty, advanced age, multiple comorbidities, deficient oral conditions, low BMI, malnutrition, involuntary weight loss, stroke, Parkinson's disease, and dementia can all contribute to dysphagia in older adults.
Awareness of these risk factors can help health care professionals and caregivers develop individualized care plans to address the specific needs of elderly patients with dysphagia and minimize the risk of silent aspiration. A speech therapist will work with the family and patient to teach special techniques that can decrease the risk for aspiration. One technique that I have see taught in minimizing aspiration is the chin tuck method. This is a simple technique that seems counter intuitive. This chin down posture , also called chin tuck technique, teaches the patient to put their chin down when they swallow their food. This closes the airway when the patient swallows. This simple technique is successful in decreasing the risk of aspiration.
Preventing Aspiration Pneumonia
Preventing silent aspiration in elderly patients is crucial to ensure their well-being and quality of life. Some effective strategies to prevent silent aspiration include modifying oral intake, providing feeding assistance, and swallowing therapy.
By implementing these strategies, healthcare professionals and caregivers can significantly reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia and its complications in older adults with dysphagia.
Modifying Oral Intake
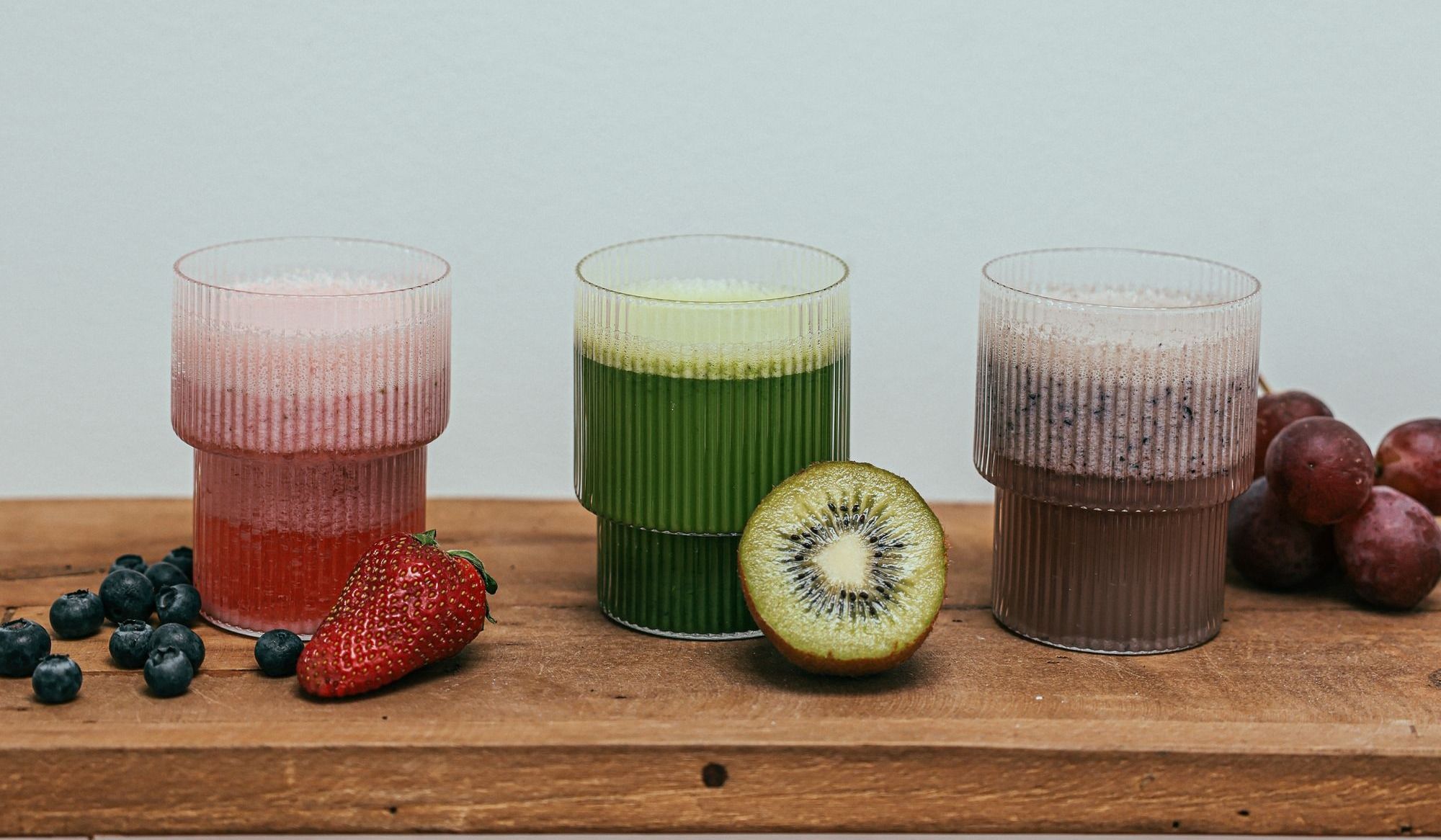

Changing the consistency of food and fluids can help prevent silent aspiration in elderly patients. Thickened liquids come in varying types of viscosity. There will be thin liquids to honey thing and many types in between. To reduce the risk of silent aspiration, it's best to feed the patient smaller amounts at a time and consider changing the consistency of their food. Avoiding sticky, stringy, dry, and chewy foods. Those with gastrointestinal intolerance to dairy products that can increase mucous, should be avoided.
Texture-modified food and liquids have been found to reduce the risk of aspiration and help residents with swallowing problems maintain adequate fluid intake. The patient's ability to stay hydrated can be challenging. Modifying oral intake not only prevents silent aspiration, but also ensures that elderly patients receive the necessary nutrition for their overall health.
Feeding Assistance
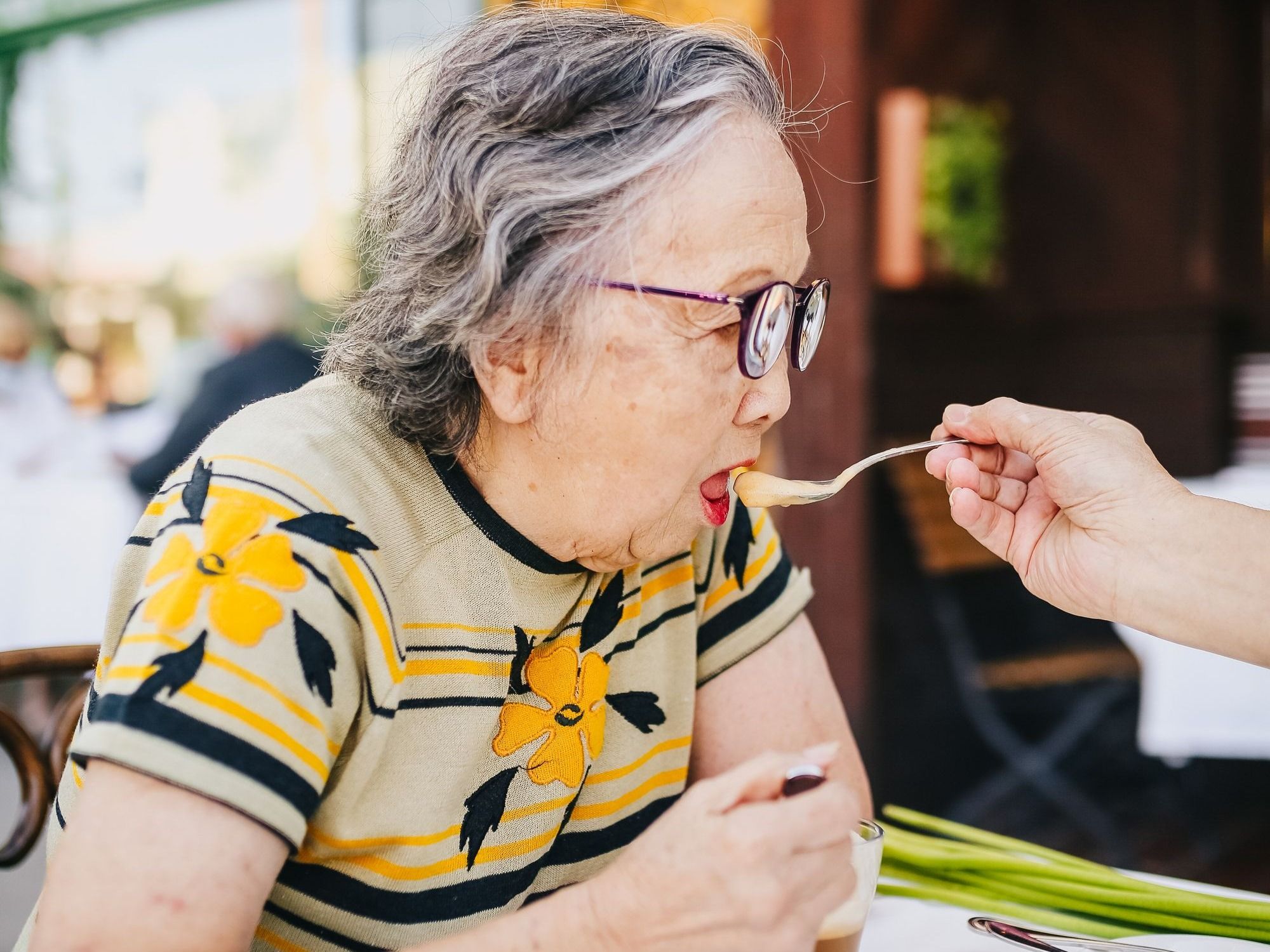

Proper feeding assistance plays a vital role in reducing the risk of aspiration in elderly patients with dysphagia. Techniques such as proper positioning, utilizing special adaptive feeding tools, and pacing feedings can be beneficial in preventing silent aspiration. Additionally, having the person sit upright in a chair, providing a 30-minute rest period prior to feeding, and slightly flexing the person's head to achieve a 'chin-down' position can help reduce the higher risk of of aspiration in some types of swallowing problems. I recommend you ask your speech therapist of the chin tuck method is appropriate for your family member.
By providing appropriate feeding assistance, health care professionals and caregivers can minimize the risk of silent aspiration and ensure that elderly patients receive the nutrition they need.
Swallowing Therapy
Swallowing therapy is a form of rehabilitation that helps individuals with swallowing probmes strengthen their swallowing ability. It may include a mix of texture modification of food/liquids, positional techniques, and compensatory swallowing strategies, as well as exercises to strengthen the muscles used in swallowing and techniques to enhance swallowing coordination.
Tongue and oral exercises, neck muscle exercises, pursed-lip breathing, coughing exercises, oromotor exercises, and vocal adduction exercises are all part of swallowing therapy. By participating in swallowing therapy, elderly patients with dysphagia can improve their swallowing ability, reduce the risk of silent aspiration, and maintain their overall health.
Medical Interventions for Aspiration Prevention
In some cases, medical interventions may be necessary to prevent silent aspiration in elderly patients. These interventions include medication management and feeding tube placement.
By implementing these medical interventions, health care professionals can further reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia and its complications in older adults with swallowing problems.
Medication Management
Certain medications can help improve swallowing ability and reduce the risk of aspiration in elderly patients with dysphagia. Medications like amantadine, levodopa, cilostazol, folate and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors have been studied for their potential to boost the swallowing reflex. Research suggests that these drugs may help enhance the reflex.
Healthcare professionals and pharmacists should closely monitor the medications taken by elderly patients with swallowing problems, as some can worsen swallowing disorders. By managing medications effectively, healthcare professionals can help reduce the risk of silent aspiration in elderly patients.
Feeding Tube Placement
Proper feeding tube placement and monitoring are crucial in preventing aspiration in elderly patients who require tube feeding. In severe cases of aspiration, a temporary feeding tube inserted can be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition until the patient can swallow more effectively. Around 20% of feeding tubes get malpositioned during routine use, which can increase the risk of aspiration.
It is essential to check the feeding tube placement every 4 hours and obtain a radiograph if the tube location is uncertain. By ensuring correct feeding tube placement and monitoring, healthcare professionals can minimize the risk of silent aspiration pneumonia and its complications in elderly patients. I recommend that you read the Pro’s and Cons of Feeding Tubes in Elderly on our site.
Caregiver Support and Education
Caregivers play a crucial role in supporting and educating individuals with silent aspiration. Being aware of the signs and symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing, coughing, or choking during meals, is essential. Caregivers should also understand the risk factors, including dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and neurological disorders. To prevent silent aspiration, caregivers can create a safe and supportive environment during meals by elevating the head of the bed, using a pillow or wedge to support the head and neck, and ensuring the individual is in a sitting position while eating. Training in swallowing exercises and techniques can also help improve the swallowing reflex, reducing the risk of aspiration. By being well-informed and proactive, caregivers can significantly contribute to the well-being of those at risk of silent aspiration.
Nursing Home and Healthcare Settings
Nursing homes and healthcare settings play a critical role in preventing and managing silent aspiration. Healthcare professionals, including speech-language pathologists, occupational therapists, and nurses, should be trained to identify and manage dysphagia and silent aspiration. Regular swallowing assessments, such as fiber optic endoscopic evaluation (FEES) or videofluoroscopy (VFS), are essential to identify individuals at risk. Nursing interventions, such as modifying the diet, using thickened liquids, and providing swallowing exercises, can help prevent silent aspiration. In cases of severe dysphagia, a temporary feeding tube may be necessary to ensure adequate nutrition and hydration. Additionally, healthcare professionals should educate caregivers and family members on how to support and care for individuals with silent aspiration, ensuring a comprehensive approach to managing this condition.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals, especially speech therapist, play a vital role in preventing silent aspiration in elderly patients. Their expertise in providing oral care, swallowing therapy, feeding assistance, and monitoring for aspiration risk is crucial in maintaining the overall health and well-being of older adults with dysphagia.
By working closely with patients, their families, and other healthcare professionals, they can develop individualized care plans that address the specific needs of elderly patients at high risk because of silent aspiration.
Speech-Language Pathologists
Speech-language pathologists are specialized healthcare professionals who play a key role in preventing silent aspiration by providing swallowing therapy for elderly patients with dysphagia. They assess patients for the presence of aspiration and suggest strategies to prevent it, such as changing the texture of food and drink and adjusting the patient's position.
By working closely with elderly patients, speech-language pathologists can help improve their swallowing ability, reduce the risk of silent aspiration, and ensure that they receive the necessary nutrition for their overall health.
Nursing Staff
Nursing staff plays an essential role in providing feeding assistance and monitoring for aspiration risk in elderly patients with swallowing problems. They can spot early signs of dysphagia and cognitive impairments, use feeding techniques and diet changes, put suctioning equipment to use, and keep the head of the bed raised after feeding.
Additionally, nursing staff can assess the patient's risk factors, such as age, cognitive impairment, and medical history, to monitor for aspiration risk. By providing appropriate feeding assistance and monitoring, nursing staff can help prevent silent aspiration and ensure the overall well-being of elderly patients with dysphagia.
Summary
In conclusion, silent aspiration is a serious issue that can lead to severe complications in elderly patients. Understanding the causes, effects disease severity, and risk factors of silent aspiration, as well as implementing strategies to prevent it, is crucial in maintaining the overall health and well-being of older adults with dysphagia. Healthcare professionals, such as speech-language pathologists and nursing staff, play a vital role in providing swallowing therapy, feeding assistance, and monitoring for aspiration risk. By working together, healthcare professionals, caregivers, and families can help prevent silent aspiration and ensure that our elderly loved ones receive the necessary care and support they need to maintain their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when you silently aspirate?
Silent aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs.
Pulmonary aspiration occurs when material such as pharyngeal secretions, food, drink, vomit, or stomach contents are breathed into the lungs without any noticeable symptoms.
These particles can cause irritation to your lungs, leading to infection, lung damage, and in severe cases, death.
How can you tell if someone is silently aspirating?
You can tell if someone is silently aspirating if they have difficulty breathing, coughing, choking, wet sounding breaths, chest pain, frequent pneumonia or bronchitis, and recurrent respiratory infections.
It's important to pay attention to these signs as silent aspiration can be dangerous and may require medical attention.
How do you stop elderly aspirating?
To prevent elderly aspiration, ensure the individual is sitting up while eating and drinking. Make sure they chew food thoroughly before swallowing. If necessary, use a wedge pillow to help them stay upright in bed while eating or drinking.
Encourage them to take small bites and sips of food/beverage, and eat slowly.
What happens when an elderly person aspirates?
When an elderly person aspirates, the material they inhale into the lungs can damage lung tissue and cause inflammation, leading to symptoms such health problems such as coughing, chest and abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, fever, and confusion.
This could eventually progress to aspiration pneumonia, making it important for elderly people to take precautions in order to avoid any aspirating.
How can a family caregiver prevent aspiration?
To prevent aspiration, a family caregiver should keep suctioning equipment close by if it has been made available. You should be trained to perform suctioning as necessary, keep the head of the bed elevated after feeding, use other feeding techniques, consult with speech therapy and follow diet modifications, and ensure proper patient positioning. The speech therapist will help you to develop an individualized care plan, specific to your family members needs. It may be learning the chin tuck, thickening liquids, or pureeing or serving soft foods.
These techniques can help reduce the risk of aspiration and ensure the patient's safety. Proper positioning is especially important, as it can help reduce the risk of aspiration and ensure the patient is comfortable. Speech therapy can also be beneficial, as it can help the patient learn how to swallow safely and effectively. Diet modifications can also help reduce the risk of aspiration.
You might also like this article:
Our Resources section can help you find the information and tools that you need. We have courses, videos, checklists, guidebooks, cheat sheets, how-to guides and more.
You can get started by clicking on the link below. We know that taking care of a loved one is hard work, but with our help you can get the support that you need.
Click here to go to Resources Section now!